Understanding Mouth Cancer Surgery
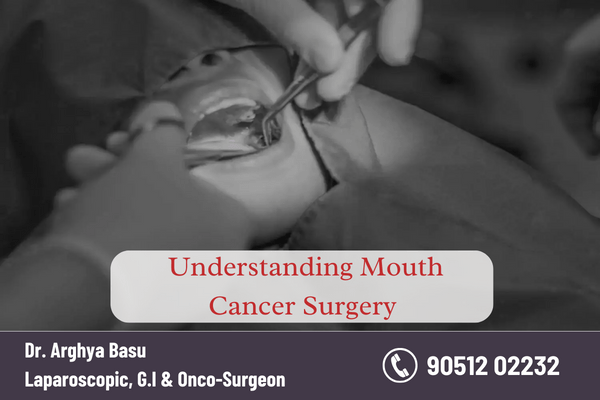
Oral cancer, also popularly known as mouth cancer in medical terminology, is a grave medical condition demanding swift and efficient intervention. One of the most crucial aspects of managing mouth cancer is surgery performed by the best cancer specialist. Within this all-encompassing guide, we shall explore the diverse facets of oral cancer surgery, ranging from its significance in treatment to the assorted surgical techniques employed.
The Significance of Mouth Cancer Surgery
1. Removal of Cancerous Tissue
The primary goal of mouth cancer surgery is completely removing cancerous tissue. This is essential to prevent the cancer from spreading to other body parts.
2. Restoration of Functionality
Surgery may encompass reconstructive techniques to restore regular functions like speech and eating, contingent upon the cancer’s location and extent.
3. Improvement of Quality of Life
Reconstructive surgery can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life after treatment. It addresses both functional and aesthetic concerns, aiding in the recovery process.
Types of Mouth Cancer Surgery
1. Excision of Tumor (Tumor Resection)
A leading oncologist carries out this procedure. It entails the removal of the tumour entirely along with the margin of healthy tissue surrounding it to guarantee thorough elimination.
2. Neck Dissection
In cases where the cancer has spread across the lymph nodes in the neck section, a neck cutting up must be performed to remove affected nodes.
3. Reconstructive Surgery
For extensive surgeries, reconstructive procedures may be necessary to restore functionality and appearance.
Preparing for Mouth Cancer Surgery
1. Consultation with Specialists
Before surgery, patients will undergo a thorough consultation with their oncologist and surgeon to discuss the specifics of the procedure and address any concerns.
2. Pre-operative Assessments
A range of tests and evaluations, including blood tests and imaging scans, will be undertaken to confirm that the patient is in prime condition for the surgical procedure.
3. Nutritional and Lifestyle Preparations
Adhering to a well-rounded diet and adopting a healthy lifestyle contribute to recovery. Patients may receive advice and recommendations from healthcare professionals to support their journey.
The Surgical Procedure
1. Anesthesia and Monitoring
Patients will be under general anaesthesia during the surgery, and vital signs will be monitored.
2. Incision and Tumor Removal
The surgeon will make precise incisions to access and remove the cancerous tissue. This process varies depending on the type and location of the cancer.
3. Reconstruction (if necessary)
In reconstructive surgery cases, the surgeon will carefully rebuild the affected area using various techniques and materials.
Recovery and Aftercare
1. Hospital Stay
The duration of the hospital stay will fluctuate based on the surgery’s intricacy and the patient’s individual recovery progress.
2. Schedule Follow-up Appointments
Scheduled follow-up appointments with the surgical team and oncologist are vital in tracking the recovery process and addressing any post-operative issues.
3. Rehabilitation and Support
Patients may undergo rehabilitation to regain functionality, and emotional support can be invaluable in recovery.
Conclusion
Mouth cancer surgery is a critical component of treatment, offering hope and a chance at a healthier future. Understanding and preparing for the process can significantly improve the overall experience for patients and their loved ones. Early detection and proactive treatment are critical factors in achieving positive outcomes. If you or a loved one is facing mouth cancer, seek professional medical advice and care promptly.
FAQ
1. How does surgery remove mouth cancer?
Oral cancer is typically addressed through surgical intervention, a pivotal component in its treatment. The surgeon makes an incision to reach the cancerous tissue in the following method. The scope of the surgery is contingent upon the cancer’s stage and location. In certain instances, the tumour is excised, whereas in more advanced cases, adjacent lymph nodes or surrounding tissues may also be removed to guarantee thorough eradication. Moreover, reconstructive surgery might be essential to restore functionality and appearance, particularly when a substantial portion of the mouth is affected. The overarching objective is to eliminate the cancer while safeguarding vital functions and aesthetic integrity.
Read More →